Stopping Power: A Deep Dive into Heavy-Duty Brake Shoes
 2025.08.19
2025.08.19
 Industry News
Industry News
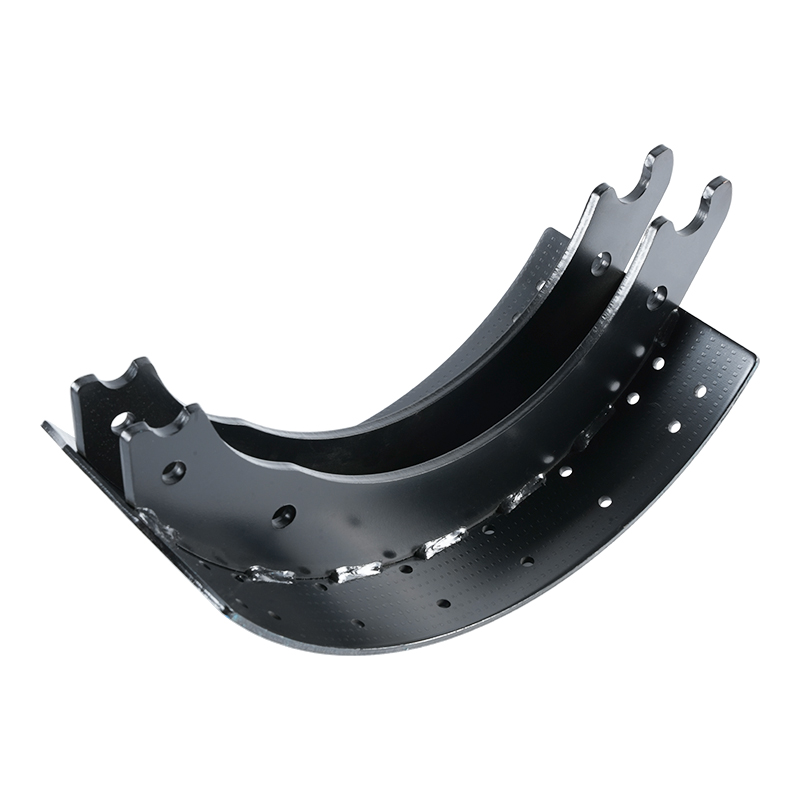
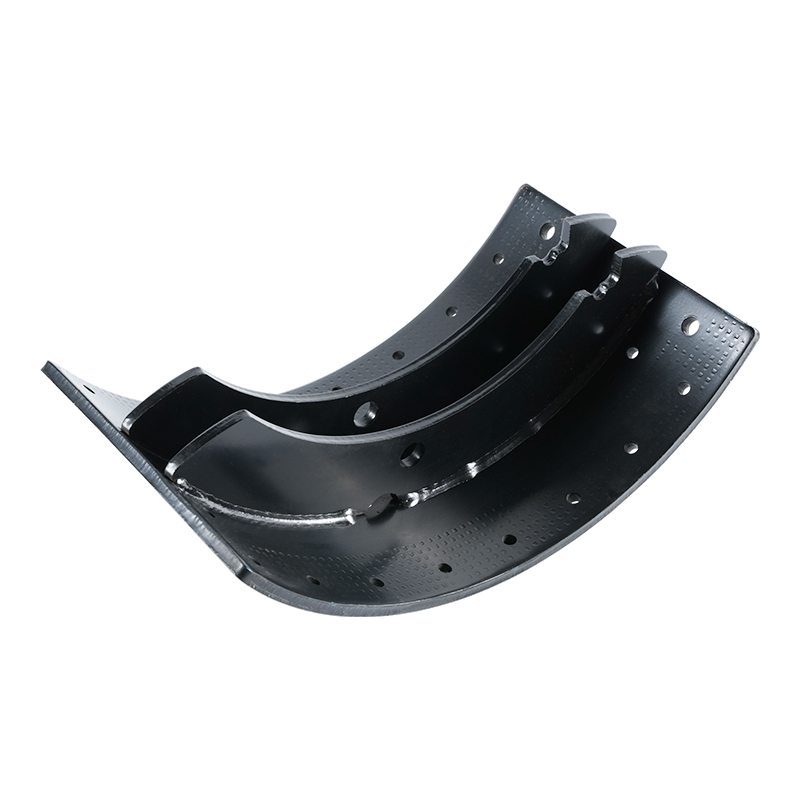
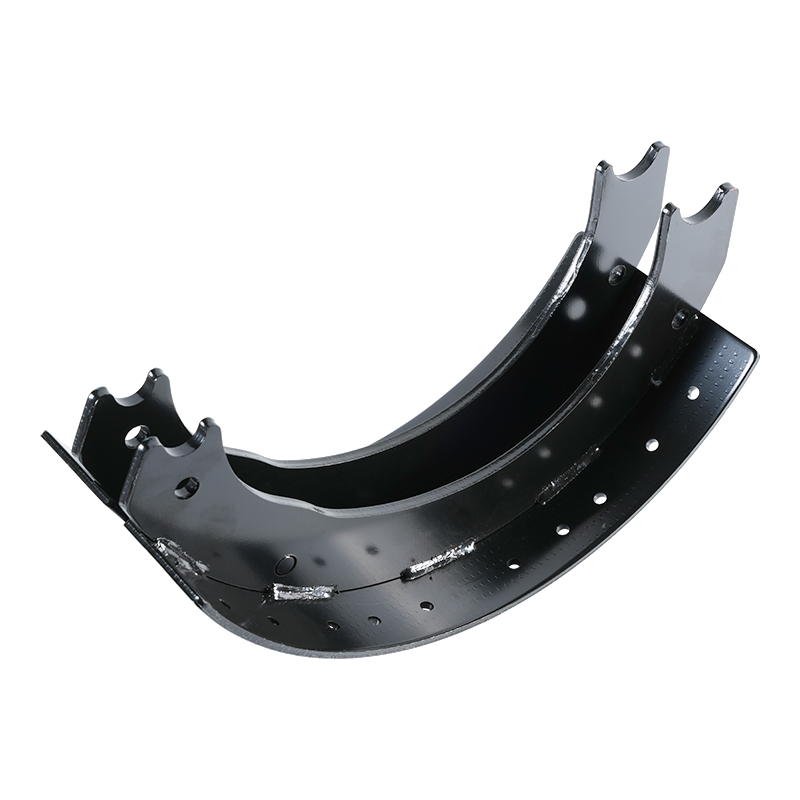
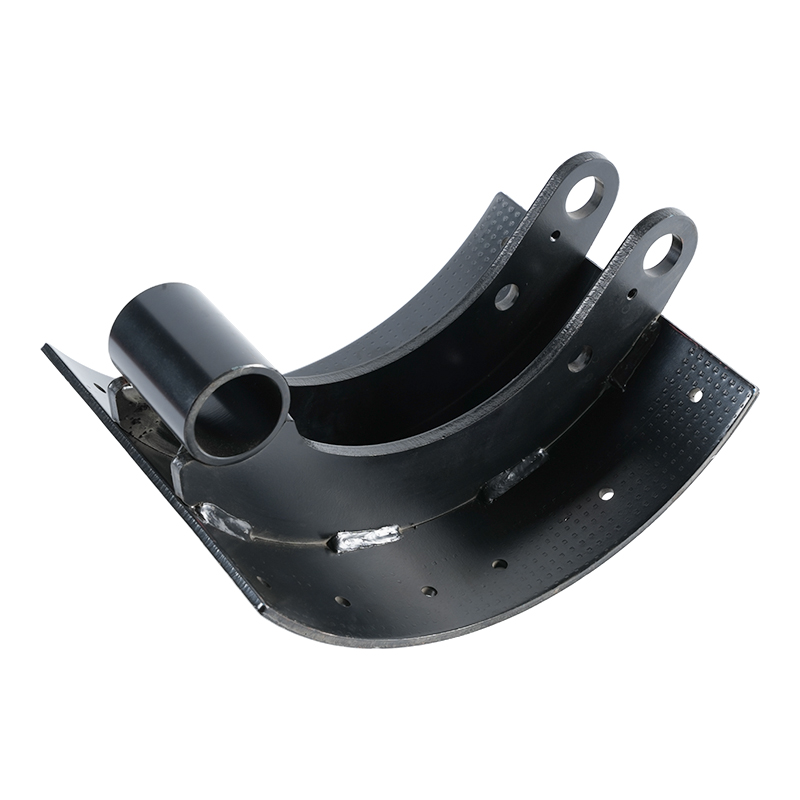
In the world of commercial vehicles, safety isn’t a luxury—it’s an absolute necessity. From the rumbling delivery truck navigating city streets to the colossal 18-wheeler traversing interstate highways, the ability to stop reliably and efficiently is paramount. While many components contribute to a vehicle’s braking system, the brake shoes stand as a fundamental and critical part, especially in heavy-duty applications. When we talk about “Heavy-Duty Brake Shoes,” we are referring to a specialized class of components engineered to withstand immense stress, heat, and friction to bring massive loads to a halt.
The Anatomy of a Stop: How Brake Shoes Work
A drum brake system, common in the rear axles of many heavy-duty trucks and trailers, relies on brake shoes to create the friction needed for deceleration. Inside the brake drum, the brake shoes are mounted on a backing plate. When the driver applies the brakes, hydraulic or air pressure forces the shoes outward, pressing their friction material against the inner surface of the rotating brake drum. This friction converts the kinetic energy of the moving vehicle into heat, slowing it down.
What Sets Heavy-Duty Brake Shoes Apart?
The demands placed on a brake shoe in a heavy-duty environment are far beyond those of a passenger car. The sheer weight of the vehicle and its cargo, combined with the frequent and often aggressive braking required for long hauls or challenging terrain, necessitates a more robust design.
-
Superior Friction Materials: The core of a heavy-duty brake shoe is its friction lining. Unlike standard linings, these are formulated with advanced, high-density materials designed to handle extreme temperatures without fading or cracking. They often incorporate a blend of synthetic fibers, resins, and other heat-resistant compounds to ensure consistent performance under punishing conditions. The goal is to maintain a high coefficient of friction even when the brakes are hot, preventing the dreaded “brake fade” that can compromise stopping power.
-
Structural Integrity: The steel shoe platform itself is built for strength. Heavy-duty brake shoes feature a thicker, more rigid construction to resist flexing and warping. This structural integrity is crucial for maintaining even contact with the brake drum, ensuring uniform wear and maximizing the life of both the shoe and the drum. A warped shoe can lead to uneven braking, noise, and premature failure.
-
Enhanced Adhesives and Rivets: The bond between the friction lining and the steel shoe is critical. Heavy-duty applications utilize industrial-grade adhesives and often a combination of adhesives and high-strength rivets to ensure the lining stays firmly in place, even under the most violent braking events. This prevents delamination, a catastrophic failure where the friction material separates from the shoe, leading to a complete loss of braking.
-
Heat Dissipation: While the friction material is designed to handle heat, the overall design of a heavy-duty braking system also plays a role in heat management. The materials and construction of the brake shoes are selected to help dissipate heat efficiently, preventing a buildup that could damage other components and reduce braking effectiveness.
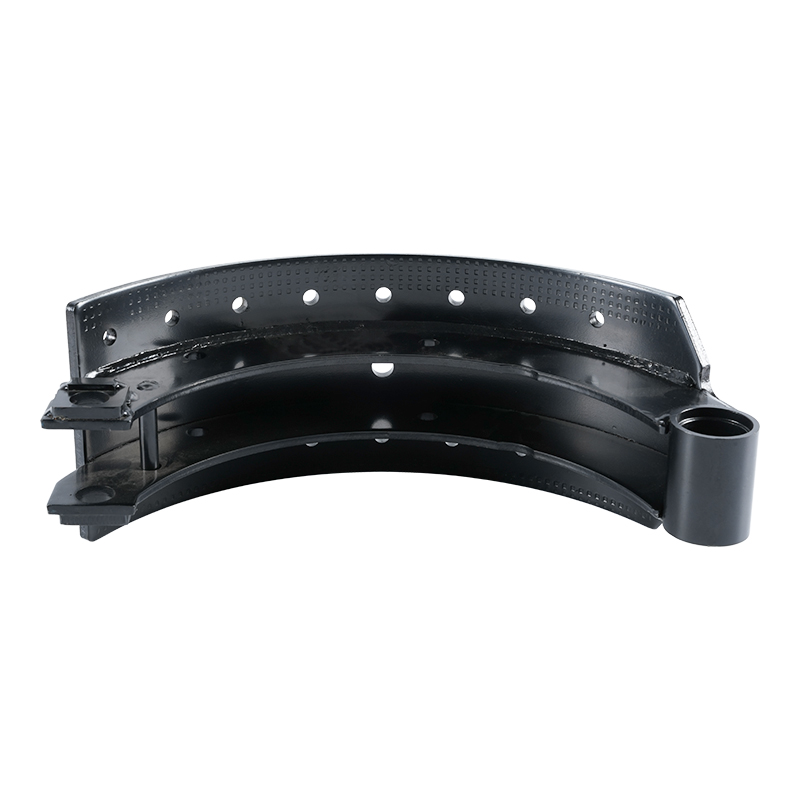

The Role of Proper Maintenance and Installation
Even the best heavy-duty brake shoes are only as effective as their installation and maintenance. Professional installation is non-negotiable, as proper adjustment and alignment are crucial for optimal performance and safety. Regular inspections are also vital. Technicians should look for signs of uneven wear, cracked linings, or oil contamination, which can significantly reduce braking efficiency.
Conclusion
In the transportation industry, every component plays a role in safety and efficiency. The humble brake shoe, when designed and engineered for heavy-duty use, becomes a critical guardian of both cargo and lives. Investing in high-quality Heavy-Duty Brake Shoes and ensuring they are maintained to the highest standards is not merely a matter of good practice—it’s a foundational element of responsible and safe commercial vehicle operation. They are the unsung heroes of the braking system, providing the unwavering stopping power that keeps the world’s goods moving safely on the road.

 Eng
Eng  中文简体
中文简体