Anatomy and Importance of the Brake Shoe Assembly
 2025.10.27
2025.10.27
 Industry News
Industry News
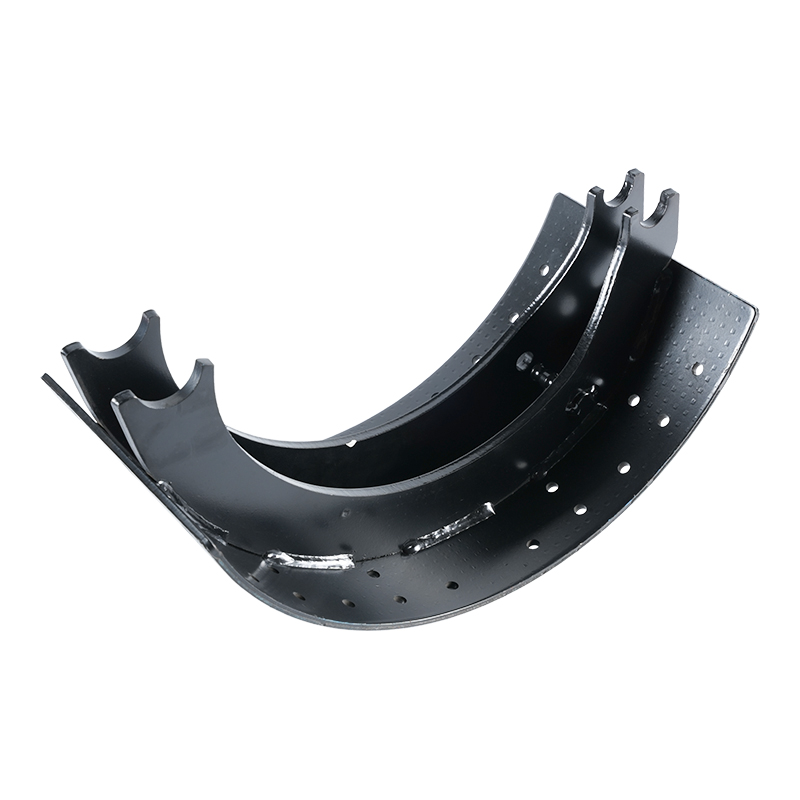
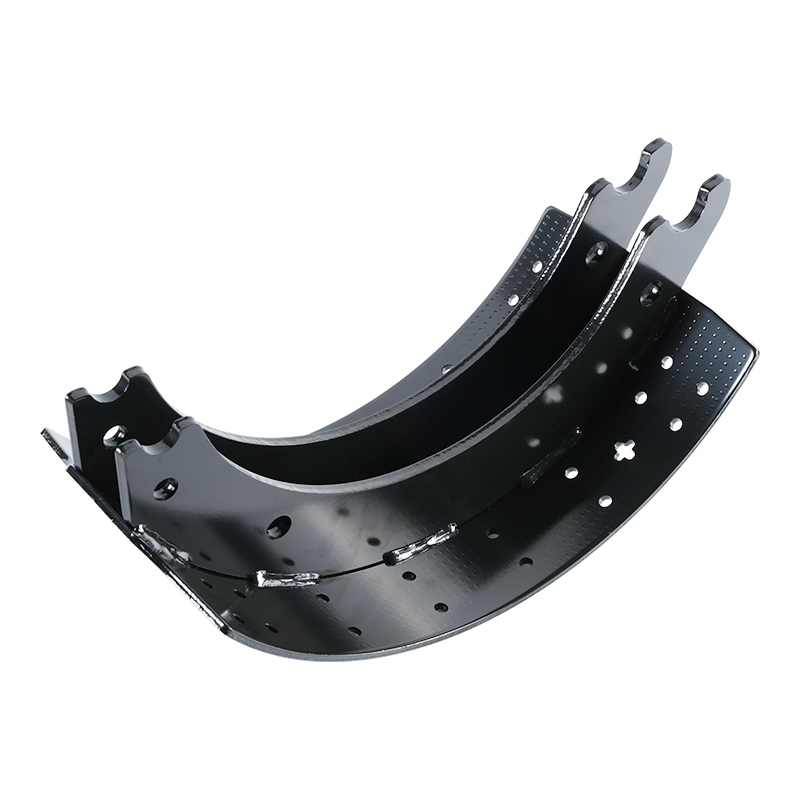
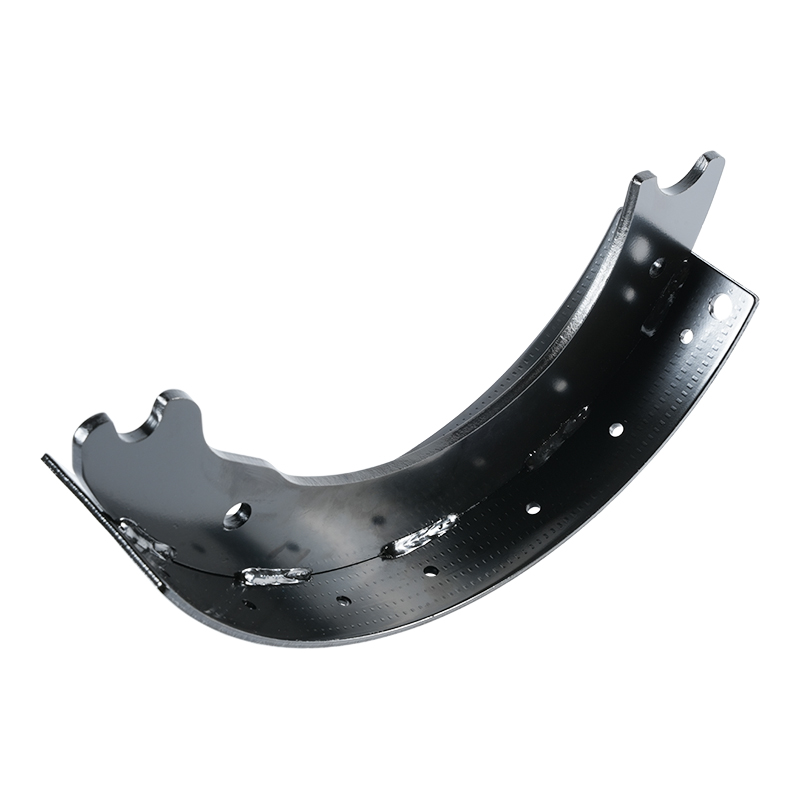
The Brake Shoe Assembly is a crucial part of the drum brake system, a foundational technology for vehicle deceleration, primarily used on the rear axles of many cars and trucks. Its reliability and simple yet effective mechanics have kept it relevant even in the age of advanced disc braking.
Function within the Drum Brake System
The primary job of the Brake Shoe Assembly is to create the necessary friction to slow the vehicle when hydraulic pressure is applied. It resides within the brake drum, which is a cast-iron cylinder bolted to the wheel hub.
When the driver activates the brakes, fluid pressure from the master cylinder pushes the pistons in the wheel cylinder. These pistons then force the brake shoes to pivot outward. The brake lining—a high-friction material attached to the curved surface of the shoes—presses hard against the rotating inner surface of the drum. This immense frictional force generates heat, converting the vehicle's kinetic energy into thermal energy and effectively bringing the wheel to a stop.
Composition of the Assembly
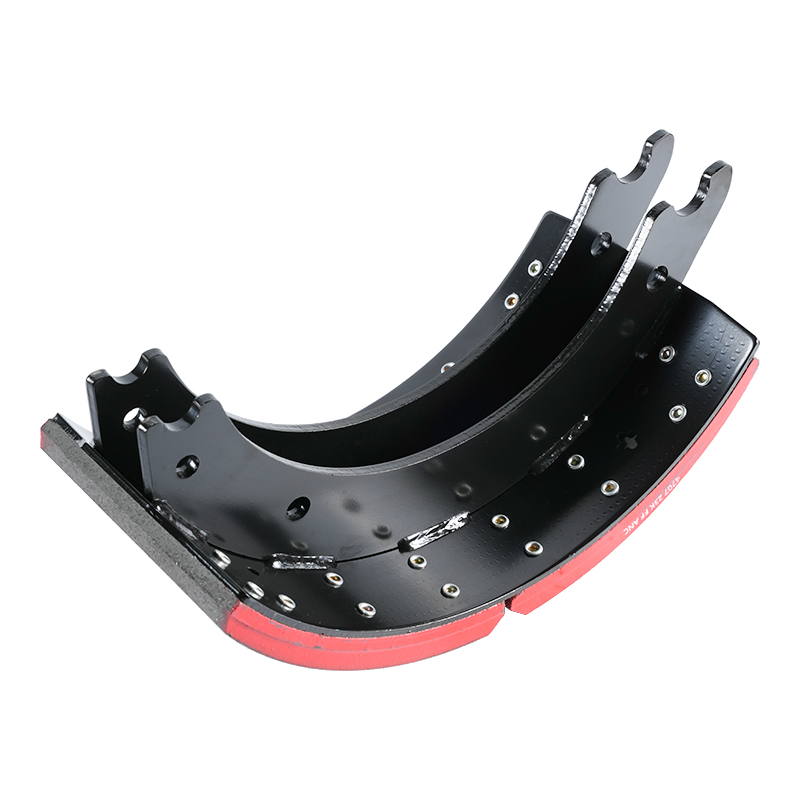
A typical Brake Shoe Assembly is not just a single part but a dynamic collective of specialized components:
-
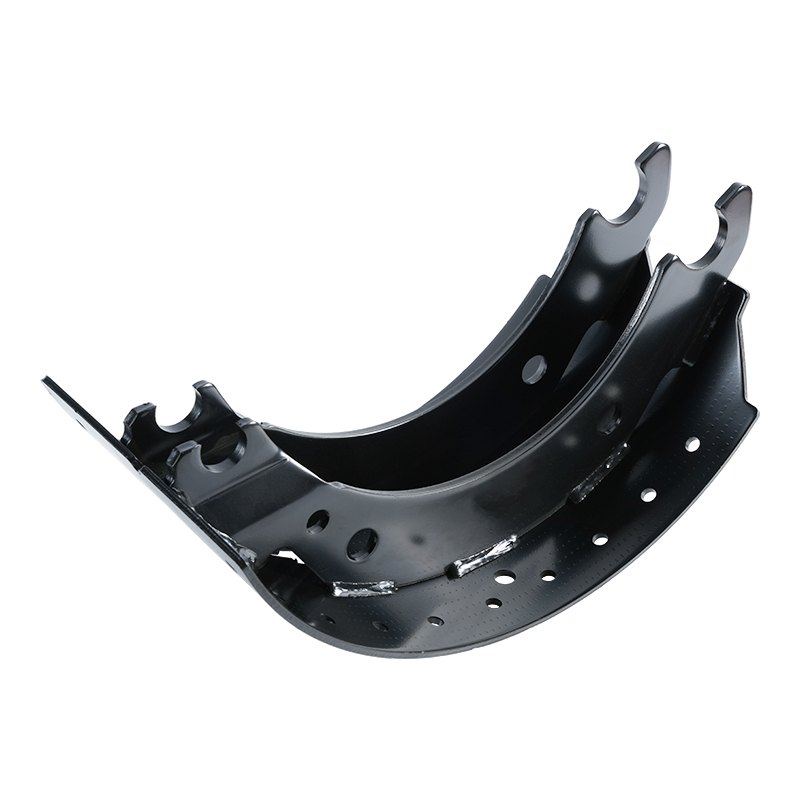
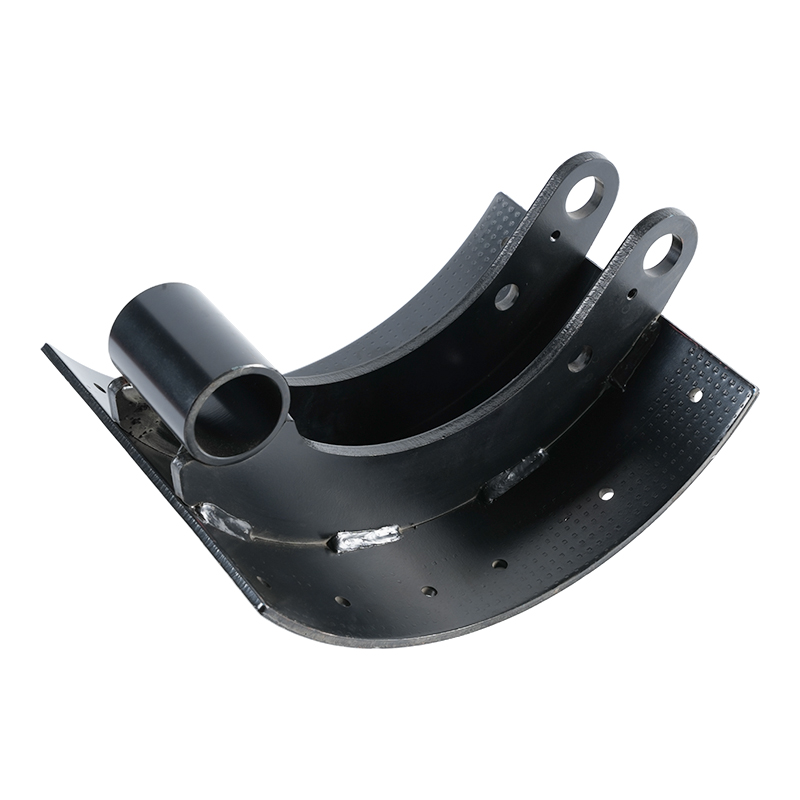
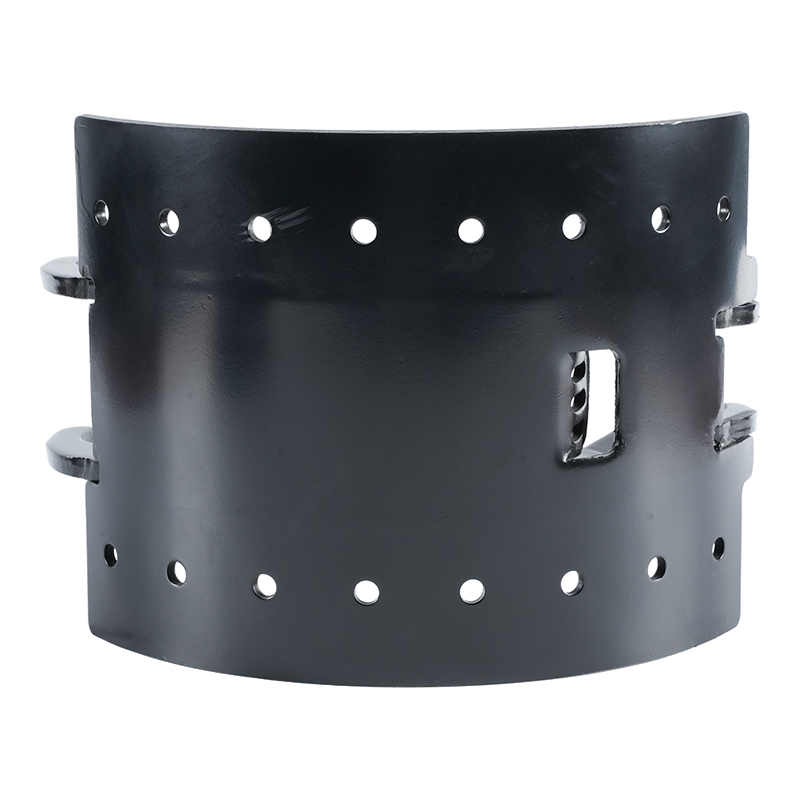
Brake Shoes: These are the strong, crescent-shaped metal pieces that serve as the foundation. They are designed to withstand the high forces and heat generated during braking.
-
Brake Lining: The vital friction material (historically asbestos, but now typically ceramic or organic compounds) that contacts the drum. Its composition dictates stopping power, fade resistance, and service life.
-
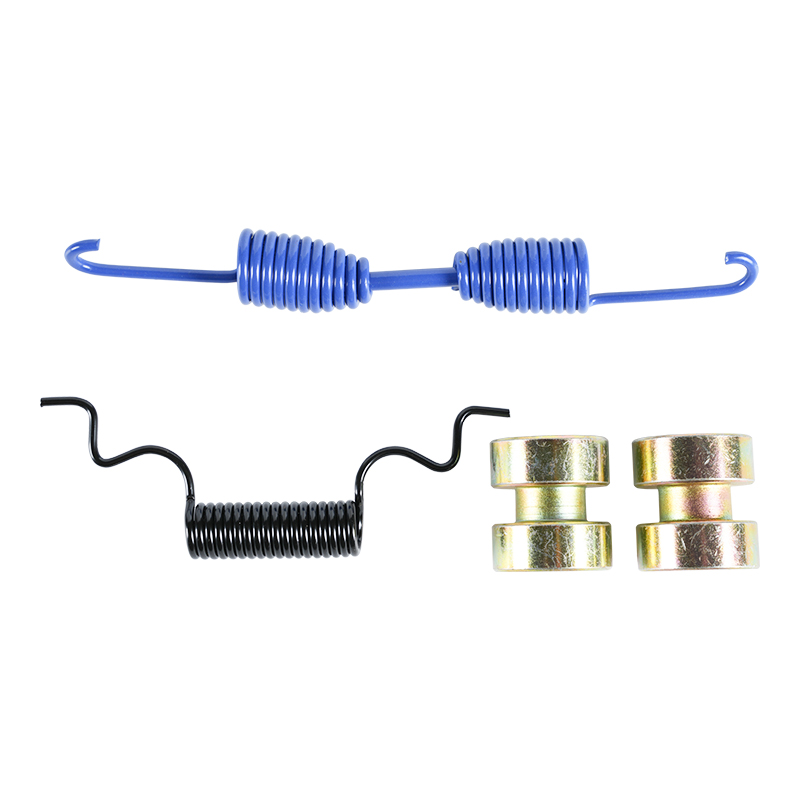
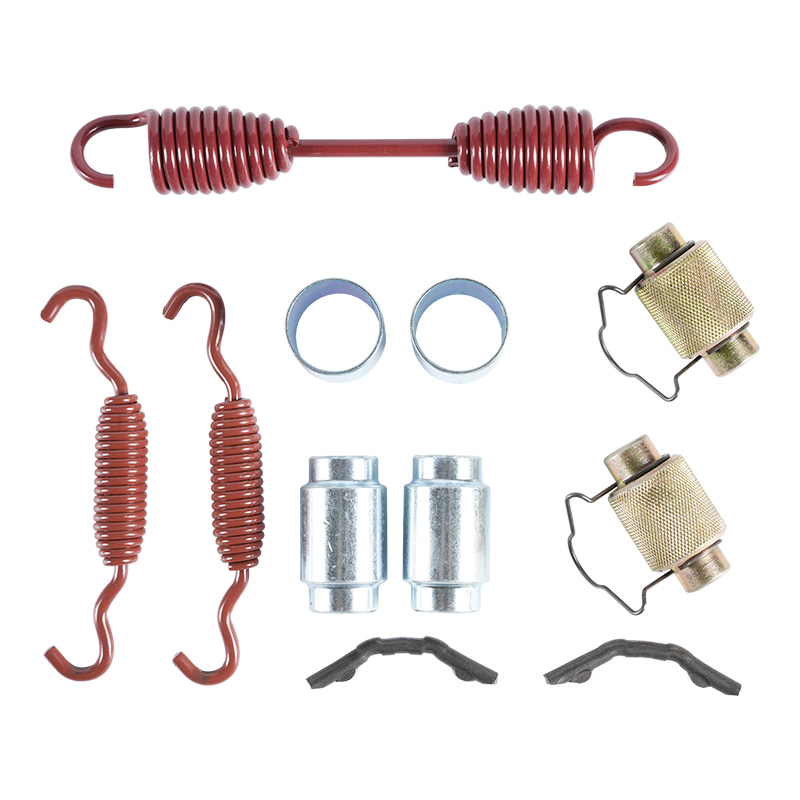
Hold-Down and Return Springs: These springs perform essential functions. The return springs pull the shoes back to their resting position immediately when the brake pressure is released, preventing continuous drag. Hold-down springs keep the shoes correctly positioned against the backing plate.
-
Self-Adjuster Mechanism: To compensate for the natural wear of the brake lining, the assembly includes an adjuster (often a star wheel and lever). This mechanism automatically senses excessive clearance between the lining and the drum and moves the shoes closer, maintaining a consistent pedal feel and effective braking.

Servicing and Longevity
The inherent design of the drum brake—with its self-energizing characteristic where one shoe's friction helps push the other into the drum—means the Brake Shoe Assembly can often have a significantly longer lifespan than front brake pads, as the rear brakes typically handle a smaller percentage of the total stopping force.
However, wear is inevitable. If a vehicle exhibits a grinding noise from the rear wheels, requires excessive travel of the parking brake lever, or experiences noticeably reduced braking efficiency, a full inspection of the Brake Shoe Assembly and its components (including the condition of the brake drum) is necessary to ensure safety and performance. When replacing the shoes, technicians must ensure the correct springs and hardware are installed to preserve the integrity of the system.

 Eng
Eng  中文简体
中文简体










